

The resistance is denoted by the rising broadening wedge’s upper line. If this support is breached, the likelihood of a further decline in coffee prices into the 180-190 region increases.

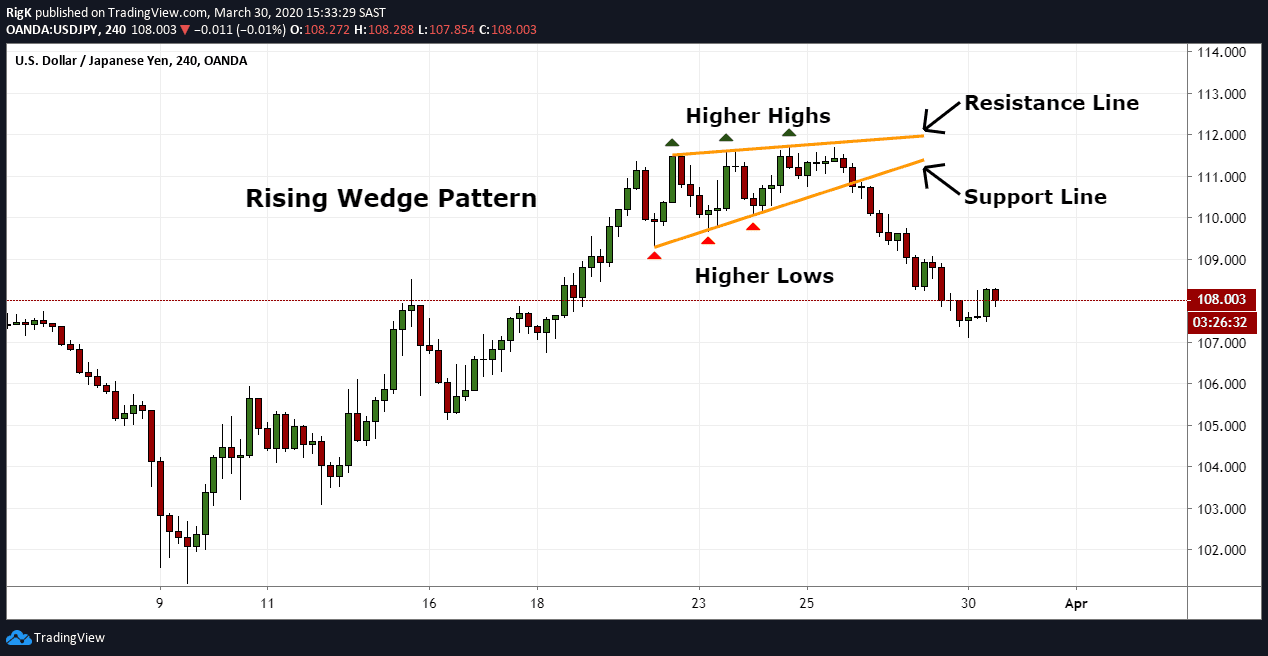
The first critical level of support is around $215 cents/lb, which was previously a triple top resistance and now is also the level at which the 50-day simple moving average hovers. Since April, the 14-day relative strength index (RSI) has been over 40, jumping a couple of times into the overbought zone. Since September 2021, coffee spot prices have traded in the ascending broadening wedge pattern mentioned above. On the daily chart, the 50-day simple moving average (SMA) is 7.5% below current prices, while the 200-day SMA is 25% lower than spot. Technically, coffee spot prices have been trading between two non-parallel trend lines, forming a so-called ascending broadening wedge – a technical chart pattern that arises in a bull market and indicates the potential for a strong reversal pattern.Ĭoffee Arabica Spot 1-day price chart as of 13 December 2021 – Credit: Coffee prices increased by about 80% in 2021 making it the second-best performing soft commodity after oat – Photo: ShutterstockĬoffee was one of the best performers among soft commodities in 2021, with an 80% gain from the start of the year, second only to oat (+93%), reaching its highest since January 2012.Ĭoffee “KC” spot contract – the world benchmark for Arabica coffee – has soared to US$235 cents/lb from $160 cents/lb of mid-July, an increase of about 50%, owing to a reduction of production in Brazil, the main producer country in the world, and supply-chain disruptions affecting trade in Asia.īrazil saw its biggest frost wave since 1994 in July, wiping off between 150,000-200,000 hectares of crops, or 11% of the country’s cultivated land.Īccording to Research and Markets, the global coffee market is expected to reach $144.68bn (£109.4bn) in 2025, expanding at a 7.60% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) between 20, owing to increased demand from emerging countries and production constraints posed by weather uncertainty.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
